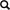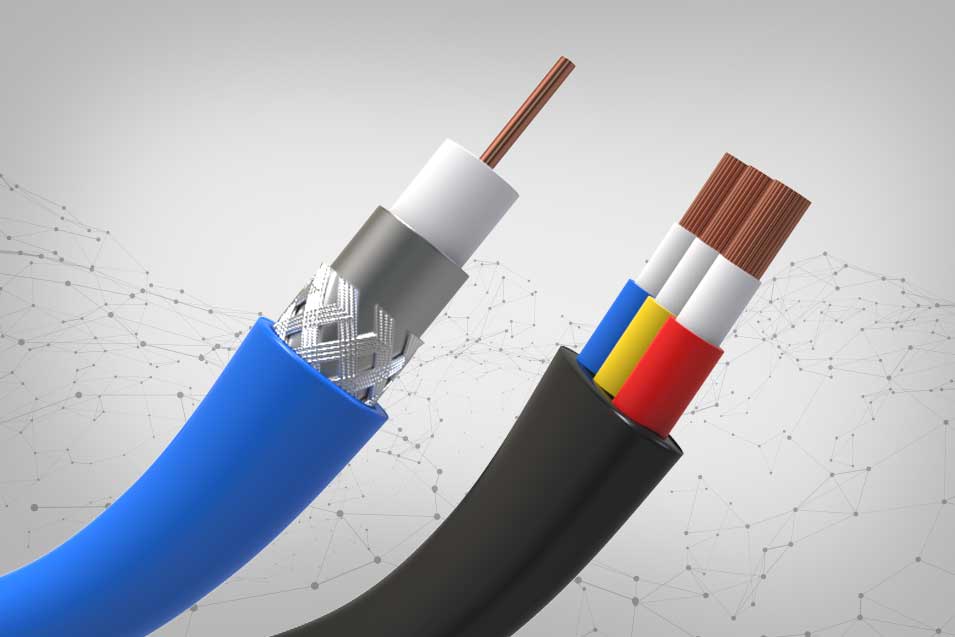
Stranded vs Braided Wire: What’s the Difference?
While considering electrical wiring multiple factors need to be taken into account, including the choice between stranded and braided wire. Both types of wires have distinctive characteristics and unique advantages, making them suitable for different environments and uses. Understanding the differences between stranded and braided wire will help you make an informed decision for your next project.
Stranded Wire
Stranded wire is composed of multiple small wires twisted together, forming a flexible and durable conductor. The multiple strands also provide a larger surface area, which can reduce resistance and improve conductivity.
- Advantages and disadvantages of stranded wire: One of the key advantages of stranded wire is its resistance to metal fatigue. The individual strands in a stranded wire can move independently, significantly reducing the risk of breakage. This attribute is particularly beneficial in applications where wires are subject to constant movement or vibration. Other advantages of stranded wires include its capability for long-distance transmission, user-friendly wiring process, and affordability.
However, connecting stranded wire to terminals and connectors can be more challenging compared to solid wire, as the strands may fray or not align properly. To mitigate this issue, soldering or specialized connectors are often used. - Uses of stranded wire: Stranded wire is commonly found in circuit board wiring, headphone cords, computer mouse cables, controller cables, and musical instruments. The flexibility and ease of use of stranded wire make it a preferred choice for residential applications.
Braided Wire
Braided wire is a type of stranded wire where the strands are intricately woven together. The braided structure provides effective electromagnetic shielding, protecting the wire from external electromagnetic interference (EMI) and preventing the wire itself from emitting EMI.
- Advantages and disadvantages of braided wire: Braided wires are a preferred choice in environments where electromagnetic interference is a problem due to their shielding property. The braiding of these wires offers additional strength and protection, making them highly resistant to physical damage, such as cuts or abrasions. Additionally, the braided design can enhance the wire’s aesthetics, which is beneficial in applications where the wire is visible and appearance matters.
Despite these advantages, braided wires are generally less flexible than non-braided, stranded wires and can be more expensive due to the complexity of their construction. - Uses of braided wires: Braided wires are widely used in noise-reduction cables and satellite cable connections. Due to its shielding properties, these wires are also used in data transmission cables and industrial settings with heavy machinery.
How to choose the right wire?
The choice between stranded and braided wire ultimately depends on your specific needs:
- Flexibility: For applications requiring a wire that can withstand frequent bending and movement, stranded wire is the superior choice.
- Durability and Protection: Braided wires possess higher tensile strength. If the wire is going to be subjected to physical stress or needs to support weight, braided wires might be the more suitable choice.
- Electrical Conductivity: While both types exhibit good conductivity, the structure of stranded wire offers slightly lower resistance owing to its greater surface area. This characteristic can be significant in high-frequency applications.
- Resistance to Metal Fatigue: Stranded wires are less prone to metal fatigue due to their flexibility.
- EMI Shielding: In environments where electromagnetic interference is a concern, braided wire offers superior shielding. Braided wires provide better EMI shielding than stranded wires.
- Installation and Handling: Stranded wires are easier to handle and install, especially in tight spaces, due to their flexibility. Braided wires, being stiffer, can be more challenging to manipulate.
- Cost Considerations: Stranded wire is generally more cost-effective, while braided wire can be more expensive due to its complex manufacturing process.
In conclusion, both stranded and braided wires have their unique advantages. Understanding the specific requirements of your project, whether it’s for home DIY, automotive, or industrial applications, will guide you in selecting the most appropriate type of wire. Remember, the right wire not only ensures the effectiveness of your project but also its safety and longevity.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) :
Q1. Are stranded wires more flexible than braided wires?
Yes, stranded wires are typically more flexible than braided wires. This is because stranded wires are made up of many small wires twisted together, allowing for greater flexibility, whereas braided wires consist of several strands of wire woven together, offering less flexibility but often greater strength and durability.
Q2. Can braided wires handle higher temperatures?
Yes, braided wires can handle higher temperatures due to their construction. This design provides improved thermal resistance and durability compared to solid wires, making them suitable for high-temperature applications.
Q3. Which wire type is more durable?
Stranded wires are generally more durable than braided wires. This is because stranded wires, composed of multiple small wires twisted together, are more flexible and resistant to breakage.
Q4. Are stranded wires prone to corrosion?
Stranded wires can be more prone to corrosion than solid wires, especially in environments with high humidity or exposure to corrosive elements. The multiple strands in these wires provide more surface area and spaces where moisture can accumulate and promote corrosion.
Q5. In what applications are braided wires preferred?
Braided wires are preferred in applications where flexibility and resistance to mechanical wear and tear are crucial, such as in electronics, automotive wiring, and aerospace industries. They are also used in shielding applications to protect against electromagnetic interference.
Q6. How does the cost compare between the two?
Typically, braided wires are more expensive than stranded wires. This is due to the more complex manufacturing process required for braiding, which often involves weaving multiple strands of wire together.